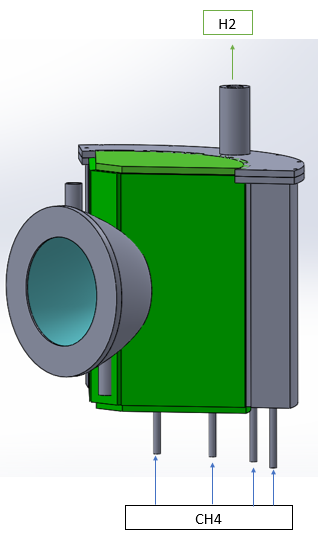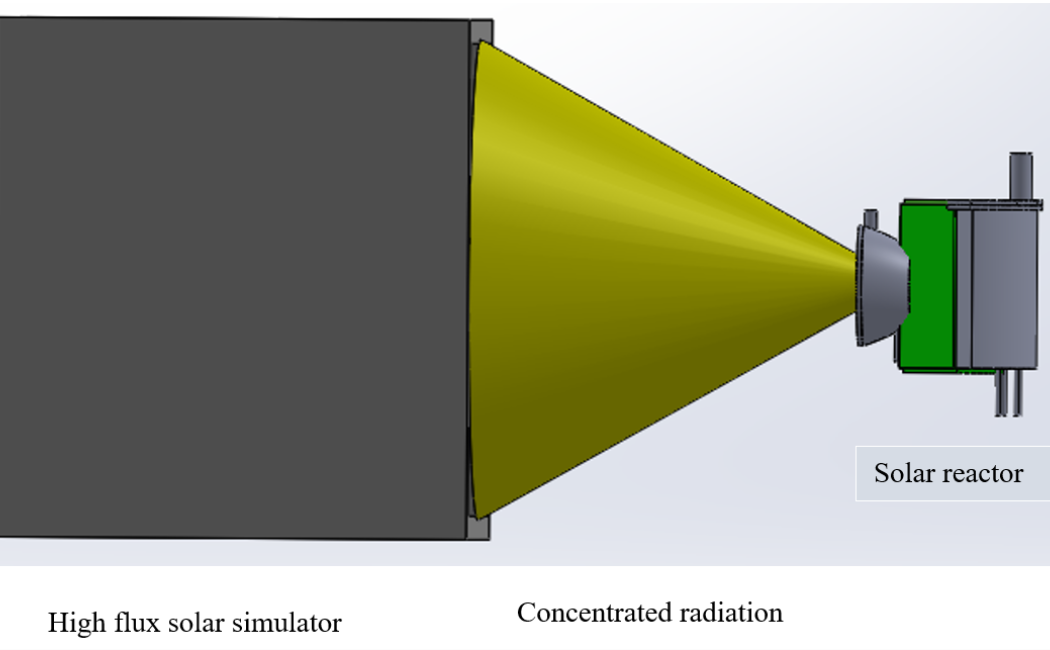
Solar natural gas pyrolysis is a concept that involves using concentrated solar energy to drive the thermal decomposition of natural gas. This process can have potential applications in renewable energy production and carbon dioxide mitigation. Indeed, conventional natural gas pyrolysis requires about 7.3-11 kWh/kg of H2. Thus, it releases 3-4.6 kg of CO2 for each kg of H2 produced. Concentrating solar thermal technology can provide the energy required for natural gas pyrolysis with near zero emissions.
A solar cavity reactor is being developed at our laboratory for natural gas pyrolysis. The process consists of: